The Truth About Cologuard Tests
Cologuard spends millions advertising its colon cancer screening product, but it’s impossible for patients to get all the information they need in a TV commercial. It’s true that it offers the benefits of comfort and convenience, but the Cologuard test is not recommended by GCSA physicians as a replacement for a colonoscopy.
Colon cancer claims over 50,000 lives every year and is the 2nd most common cause of cancer death in the US. Colon cancer is preventable, treatable, and beatable – but only with early and accurate detection.
Any colon cancer screening is better than no screening, but patients should know the pros and cons before making a final decision.
What is a Screening Test?
Screening tests are done to detect potential problems in people who do not have any symptoms of disease. The goal of screening is to provide early detection, reduce the risk of disease, and treat the condition more effectively. For colon cancer, in particular, finding and removing polyps can actually prevent cancer from forming. Polyps are small lumps of tissue in the colon and rectum that may turn into cancer over time.
Types of Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Screening
Because colon cancer begins as growths called polyps, finding and removing polyps is the best way to prevent colon cancer. There are three types of CRC screening:
- Colonoscopy – 95% of large polyps detected
- Stool DNA (Cologuard Test) – 42% of large polyps detected
- Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) – 24% of large polyps detected
Colonoscopy is the gold standard for finding polyps. If polyps are found during a colonoscopy, they are removed during the same single procedure. This eliminates the need for additional procedures or tests.
If polyps are found through FIT or a Cologuard test, a colonoscopy must be performed to remove the polyps.
Unfortunately, the majority of large polyps go undetected with stool-based tests. When polyps aren’t found and removed, it increases the risk of developing colon cancer.
Cologuard Test: Detection Not Prevention
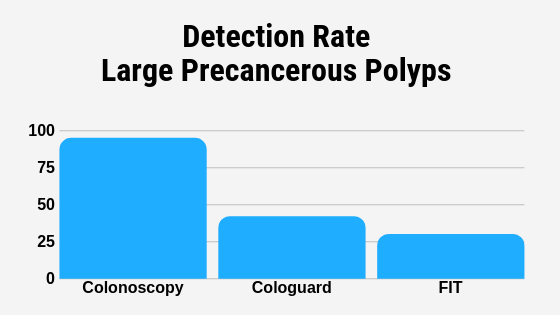 The Cologuard test is designed to detect cancer not prevent it. It can only detect 42% of large polyps, while a colonoscopy can detect 95% of large polyps.
The Cologuard test is designed to detect cancer not prevent it. It can only detect 42% of large polyps, while a colonoscopy can detect 95% of large polyps.
When polyps are detected during a colonoscopy, they are removed at the same time. If polyps are detected with a stool test, a colonoscopy must be performed to remove them.
The majority of large precancerous polyps cannot be detected with Cologuard. This may give patients a false sense that they are preventing colon cancer by taking the test, when in fact they may already have cancer and not know it.

Save Time & Money
If you have a high risk of colorectal cancer, which includes:
- a family history of colon cancer
- present symptoms
- previous colonoscopy finding of polyps
You should skip the Cologuard test.
This will save you time, money, and the frustration of undergoing both tests since a colonoscopy is needed for high-risk patients. Plus, if Cologuard results are positive, you’ll need a colonoscopy anyway.
If your primary care provider recommends a stool test, and you are at high risk, you should consult with a specialist before undergoing the test.
How does the Cologuard test work?
The Cologuard test is a less reliable stool DNA test that looks for microscopic blood in the stool and altered DNA. It’s performed using an at-home kit that includes a container for a stool sample. That sample is then shipped to a lab for testing.
Is Cologuard accurate?
Cologuard can detect 92% of cancers but only 42% of large precancerous polyps. In other words, no, it is not accurate, especially when it comes to preventing cancer by detecting polyps.
While it is better at detecting cancer than FIT (74% vs 92% for FIT test vs Cologuard), the false positive rate is higher. The Cologuard false-positive rate is 13%, and that rate increases as people age.
Cologuard is less accurate than a colonoscopy at detecting polyps of any size. A colonoscopy can detect 95% of large polyps but the stool test only detects 42%.
These statistics are referred to as sensitivity and specificity, or the confidence that a positive test is truly positive and a negative test is truly negative. The test’s specificity and sensitivity aren’t as good as a colonoscopy.
Cologuard FAQ
Can Cologuard detect polyps?
Yes, it can detect polyps. However, the detection of large polyps (the precursors to colon cancer) is less than half as accurate as a colonoscopy.
Is the Cologuard test as effective as a colonoscopy?
No, it is not as effective as a colonoscopy. Detecting and removing polyps is critical to colon cancer prevention, and the test only detects large precancerous polyps 42% of the time. A colonoscopy detects the same polyps 95% of the time and they are removed during the same procedure.
What does a positive Cologuard test mean?
If you have a positive test, it may mean that colon cancer or polyps are present. After a positive Cologuard test, a colonoscopy is required for a definitive answer. The Cologuard false positive rate is 13%, which means 1 in 10 positive tests will incorrectly identify cancer or polyps.
Can Cologuard detect cancer?
Yes, the Cologuard test can detect cancer 92% of the time. However, prevention of colon cancer is better than identifying it once you have it. The best way to prevent colon cancer is by identifying and removing precancerous polyps that don’t turn into cancer later. Cologuard only finds 42% of large, dangerous polyps that can turn into colon cancer.
Can I use Cologuard instead of a colonoscopy?
Cologuard is not designed to be a replacement for a colonoscopy, even though advertisements may suggest otherwise. 58% of the time, dangerous precancerous polyps are not detected with the test, which is significantly less effective than a colonoscopy. However, it may be an option for some patients who insist on not getting a colonoscopy or those not healthy enough to have a colonoscopy. Even a 42% chance of detection is better than no detection at all.
How long is Cologuard good for?
This particular test should be done every three years rather than annually due to the higher cost and false-positive rates compared to an annual FIT. More research is needed to determine how often the test should be done.
What is the false positive rate of Cologuard?
The false-positive rate for Cologuard is 13% or a little over 1 in 10.
Is a stool sample as good as a colonoscopy?
FIT and Cologuard tests performed using stool samples are not as effective at identifying the large precancerous polyps that lead to colon cancer. FIT and Cologuard tests are more effective than doing no testing at all.
How accurate is stool test for colon cancer?
There are two types of stool tests for colon cancer. Fecal Immunochemical Test (FIT) and Stool DNA (Cologuard). FIT detects 74% of colon cancers and 24% of large colorectal polyps. Stool DNA detects 92% of cancers and 42% of large colorectal polyps.
How much does Cologuard cost?
The cost is around $500. Some insurance plans may cover part of that cost depending on your plan, co-pay, and deductible. Diagnostic testing is subject to deductibles and coinsurance.
Screening colonoscopies are not subject to copays and deductibles and usually have no out-of-pocket costs for patients.
Is Cologuard Cost Effective?
A recent study looked at the effectiveness and cost of different colon cancer screening options and the results were clear: Cologuard was less effective and more expensive than other screening options.
What can Cologuard detect?
The test can detect 92% of cancers and 42% of large precancerous polyps, the precursor to colon cancer.
Who is Cologuard good for?
Cologuard may be an option for patients who insist on not having a colonoscopy or who are not healthy enough for the procedure. Some patients may decide that the risks associated with a colonoscopy outweigh the benefits of increased detection.
Any test for colon cancer is better than no test at all. If the test is positive, a colonoscopy will be necessary.
What are common misspellings of Cologuard?
Collguard, Cholegard, and Colorguard are common misspellings.
Request Appointment
Sources: American Society of Gastroenterologists and Cologuard.com
Related:



